Precision, Variability, and Accuracy of Femoral Varus Measurement
 Monday, April 23, 2012 at 06:00AM
Monday, April 23, 2012 at 06:00AM Alexander C. Robb
Cummings School of Veterinary Medicine at Tufts University
Precision, Variability, and Accuracy of Femoral Varus Measurement Using Radiographic and Computed Tomographic Imaging in Clinically Abnormal Femora
INTRODUCTION: Many skeletal abnormalities have been associated with medial patellar luxation (MPL), and recent focus has centered on femoral malalignment, specifically excessive femoral varus, quantified by measurement of the anatomic lateral distal femoral angle (aLDFA).1,2 In cases with excessive varus, a distal femoral osteotomy can be performed; however, this invasive procedure requires accurate measurement of aLDFA. Recent studies have reported conflicting evidence regarding the ability to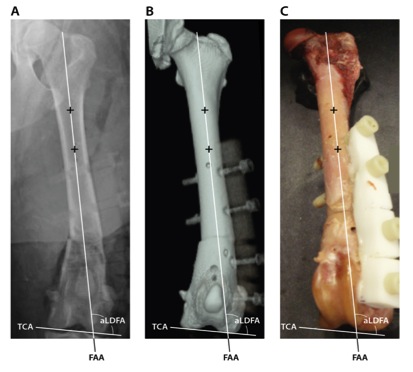 measure distal femoral varus in clinically normal bones using both radiographic and computed tomographic (CT) methods.1,3 The purpose of this study was to establish the precision, variability, and accuracy of aLDFA measurement using radiographic and CT imaging, compared to the reference standard of digital photographs of anatomic specimens, in clinically abnormal femora. Our hypothesis was that CT would be more precise, less variable, and more accurate than radiographs for aLDFA measurement.
measure distal femoral varus in clinically normal bones using both radiographic and computed tomographic (CT) methods.1,3 The purpose of this study was to establish the precision, variability, and accuracy of aLDFA measurement using radiographic and CT imaging, compared to the reference standard of digital photographs of anatomic specimens, in clinically abnormal femora. Our hypothesis was that CT would be more precise, less variable, and more accurate than radiographs for aLDFA measurement.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: Ten skeletally mature dogs weighing 20-40 kg euthanized for reasons unrelated to this study were used for analysis. Specimens were disarticulated proximal to the lumbar 5th/6th intervertebral disk space. A craniocaudal radiograph of each femur was obtained and the aLDFA was calculated. Each femur was randomly assigned a wedge size between 9 and 19 degrees, sufficient to induce clinically relevant varus. A medially based wedge osteotomy of the distal femur was performed, and the femur was stabilized with custom fabricated radiolucent Delrin plates and radiolucent glass-filled nylon screws. Three craniocaudal images of each femur were obtained using radiography, three-dimensional reconstruction of transverse CT images, and photography. Criteria for acceptable positioning were as described by Dudley.3 For each modality, one observer determined acceptable positioning for each image. The images were cropped to remove any identifying information, listed in a random order, and each evaluator measured aLDFA from every image in triplicate. Evaluators included a board-certified surgeon and a third-year veterinary student. The aLDFA was determined as previously described by Tomlinson.2 Precision was defined as the extent (in degrees) to which multiple measurements of the same image made by the same observer agreed. This was determined by calculating the mean standard deviation of aLDFA measurements for each individual image by modality. Pairwise comparisons were made with a matched-pairs Wilcoxon signed rank test. Variability was defined as the variation (in degrees) contributed by capturing multiple images and measuring aLDFA multiple times from each image. This was determined by calculating the mean standard deviation of measurements made for each bone, averaged by observer and modality. Pairwise comparisons were made using a matched-pairs Wilcoxon signed rank test. The average aLDFA measurements for each modality were compared using a paired t-test to evaluate accuracy. For all analyses, statistical significance was set at a value of P<0.05.
RESULTS: The precision of CT measurements (mean SD = 0.701°) was greater than that of radiographs and photographs (P<0.001), and the precision of photographs (mean SD = 0.943°) was greater than radiographs (mean SD = 2.289, P< 0.001). The average variability in measurements made from radiographs (3.019°) was significantly greater than the variability in measurements made from photographs (1.485°, P<0.001) and CT (1.224°, P<0.001). Conversely, the variability in measurements made from CT was not significantly different than that of the photographs (P=0.18). The findings of low precision and numerically greater variability in the photographic reference standard precluded true determination of accuracy, thus the results of the paired t-tests were considered to determine if one method was systematically different than another. No systematic difference was identified between any of the modalities (Radiographs-Photographs: Average Mean Difference =1.659°, P=0.123, CT-Photographs: Average Mean Difference =0.7780°, P=0.511, Radiographs-CT: Average Mean Difference =0.8813°, P=0.255).
DISCUSSION: The finding that there was no systematic difference between any of the modalities in this study lends support for the use of both radiographs and CT in measurement of clinical cases. However, the lack of precision and greater variability in measurements made from radiographic images indicates that this is not the ideal method. Based on our findings, it appears that CT is the best diagnostic method of the imaging modalities evaluated, since it is the most precise and least variable. These findings support the use of CT for imaging clinical cases, and for use as a reference standard in research investigations. Since the photographic method was found to have significantly lower precision and numerically greater variability, its use as a reference standard in future studies should be questioned. A range for normal canine aLDFA established using CT would be useful to guide the clinician in accurately diagnosing and treating clinical cases. A limitation to this study is that only one investigator captured the images for each modality, eliminating a source of variability; however, this does not represent a realistic clinical scenario. A future investigation examining variability in radiographs and CT performed by different investigators would be beneficial.
REFERENCES: 1. Swiderski, Jennifer K. et al.: Comparison of radiographic and anatomic femoral varus angle measurements in normal dogs. Vet Surg 37:43-48, 2008. 2. Tomlinson, James, et al.: Measurement of femoral angles in four dog breeds. Vet Surg 36:593-598, 2007. 3. Dudley, Robert M., Michael P. Kowaleski, et al.: Radiographic and computed tomographic determination of femoral varus and torsion in the dog. Vet Radiol Ultrasound 47:546-552, 2006.
 Tufts in
Tufts in  Cases/Abstracts
Cases/Abstracts 
Reader Comments